Simufact Forming
Gespecialiseerde vormsimulatiesoftware voor virtueel testen en procesontwerp om componenten te optimaliseren
Metal Forming Excellence
Advanced simulation software orchestrates metal forming, unlocking the art of successful cold forming, hot forging, rolling, and stamping.
Softwareoplossing voor vormprocessen zonder deskundige kennis
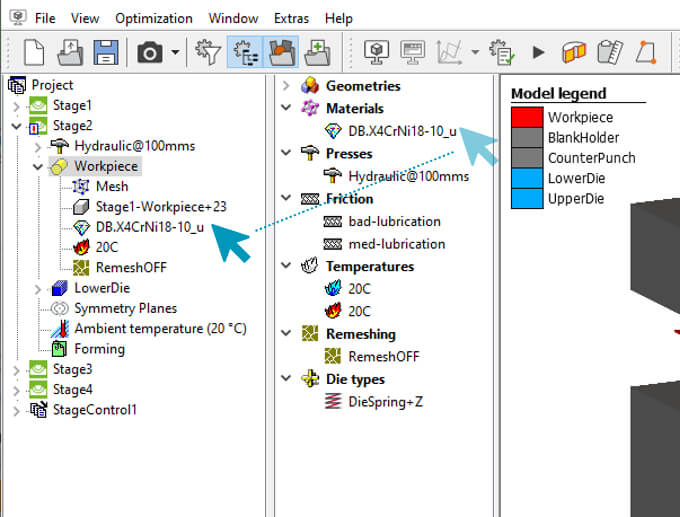
![]() Simufact Forming is een simulatietool voor de beoefenaar van vormtechnologie. Onze belofte is om de software consequent af te stemmen op de praktische behoeften van de gebruiker.
Simufact Forming is een simulatietool voor de beoefenaar van vormtechnologie. Onze belofte is om de software consequent af te stemmen op de praktische behoeften van de gebruiker.
Vaak is deskundige kennis nodig om simulatieomgevingen te bedienen om complexe modellen te bouwen en te programmeren. Dit is niet het geval bij Simufact Forming. De gebruiker hoeft zich niet bezig te houden met de grijze fysica van het vormingsproces of met simulatiespecifieke details. Simufact Forming is praktisch en kan snel en eenvoudig worden geleerd. De beoefenaar van vorming kan zich dus concentreren op de details van zijn vormprocessen in plaats van op de software.

"Zo eenvoudig mogelijk – zo complex als nodig"
De gebruikersinterface van Simufact Forming is ontwikkeld om eenvoudig, intuïtief en procesgericht te zijn. Hierdoor is Simufact Forming een ontwerptool voor de tool- en procesontwikkelaar, die het dagelijkse werk van de gebruiker ondersteunt en vereenvoudigt. Met slechts enkele muisklikken kunnen alle standaard vormingsprocessen worden ingesteld en geëvalueerd:
- Koudvervorming
- Warm smeden
- Plaatmetaalvorming
- Walsen
- Rondwalsen
- Stampsmeden
- Hittebehandeling
- Mechanisch koppelen
- Druklassen
Klik hier voor meer informatie over de afzonderlijke procestypen.
Uw voordelen met Simufact Forming
- Ontwerp en optimaliseer uw vormingsproces:
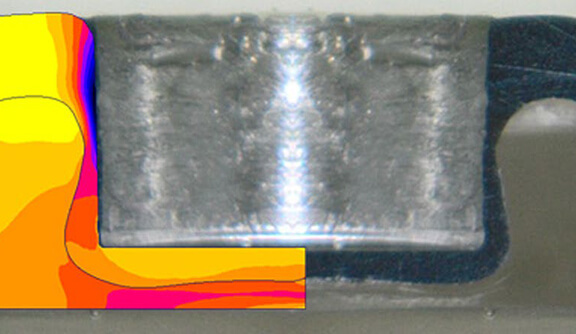
- Bepaal het optimale aantal en de optimale volgorde van fasen en procesvensters met een minimaal materiaalverbruik en zorg tegelijkertijd voor een robuust productieproces.
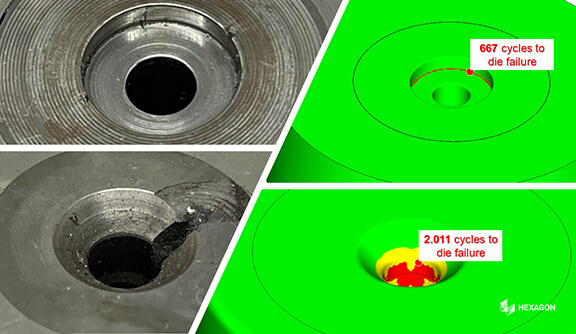
- Potentiële productiefouten identificeren en elimineren
- Levensduur van gereedschappen optimaliseren
- Eenvoud – Geen deskundige kennis vereist, omdat de softwareoplossing gebruiksvriendelijk, intuïtief en procesgericht is.
- Duurzaamheid – Bespaar materiaal, tijd en geld door dure en tijdrovende fysieke tests te vervangen door virtuele tests.
Lees meer over de functies en toepassingsgebieden op de Simufact-website.
Exactly the right forming process you need
Forming processes conducted significantly below the recrystallisation temperature of the material. These processes include typical upsetting and extrusion processes (e. g. for the production of bolts, nuts and rivets), but can also include coining, cold hobbing, thread rolling and last but not least drawing processes (e. g. wire drawing, tube drawing and profile drawing).
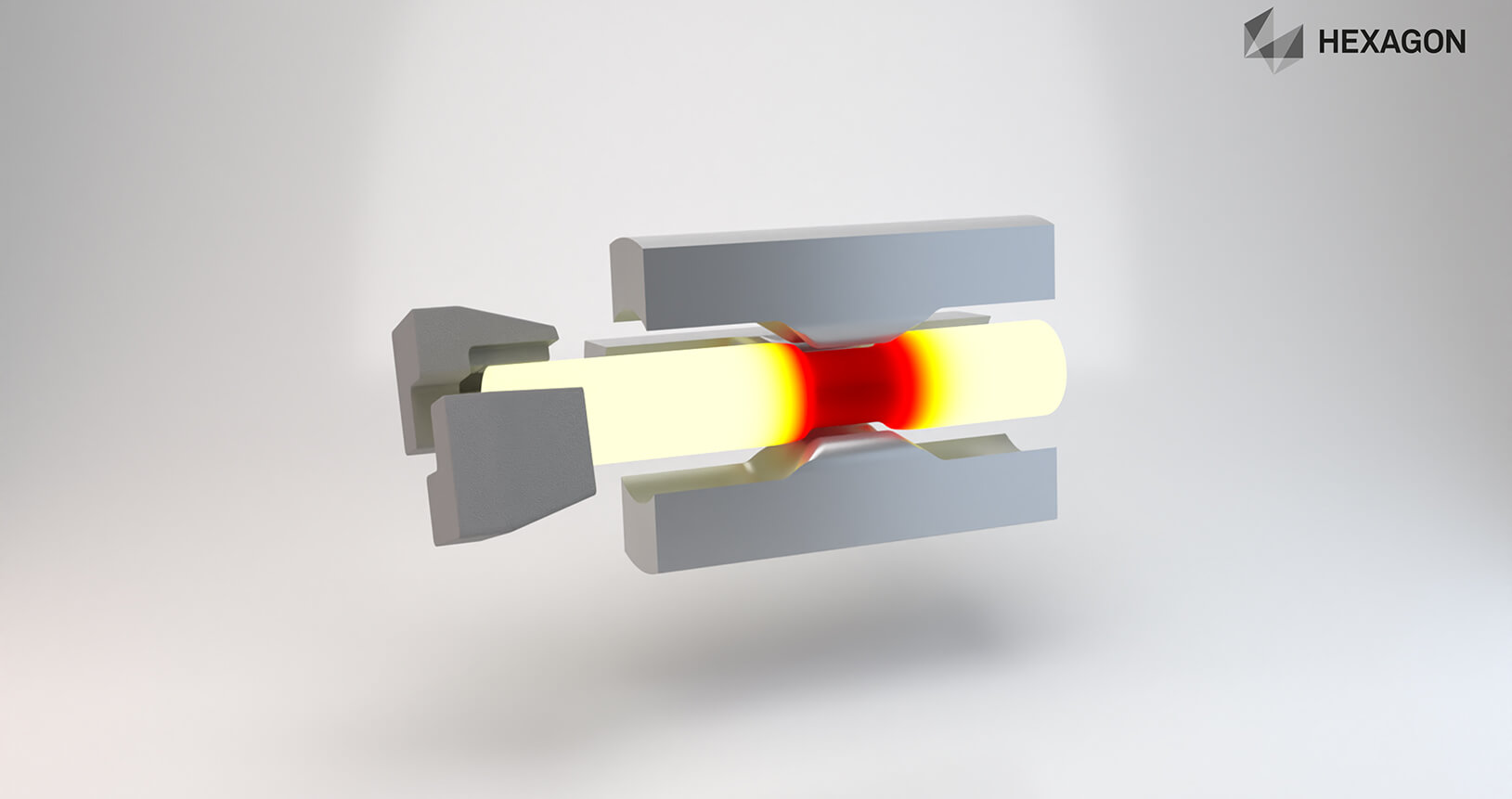
Forming processes conducted above the recrystallisation temperature of the material. A typical process is hot forging, including closed die hot forging, auxiliary processes such as heating and cooling, cutting processes and preform operations (e. g. upsetting, bending, forge rolling and cross wedge rolling) as well as extrusion processes.
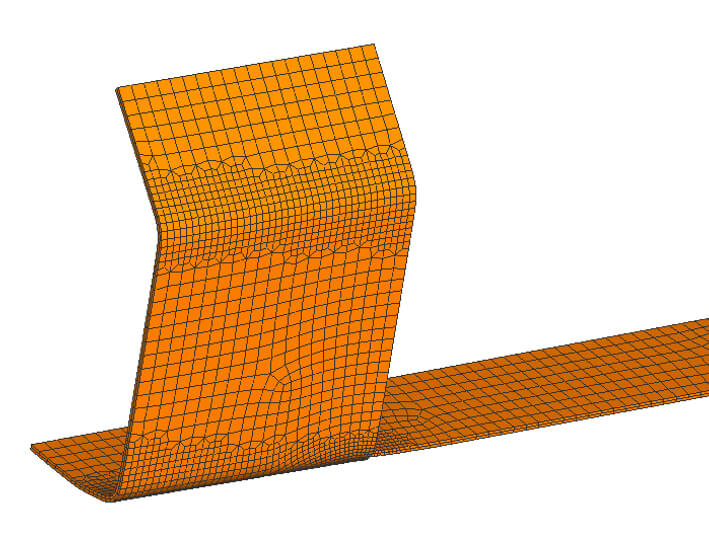
Different methods of sheet metal forming can be used depending on the geometry of the desired part. Based on the characteristics of each deformation process, the forming engineer can choose between: Deep drawing, ironing, punching, bending, stamping, and a variety of other manufacturing processes. Due to the geometric complexity of the parts being manufactured, additional multistage forming that combines different processes is frequently required within a phase of production. Therefore, production is usually achieved by automated transfer or stage pressing, or by progressive tools.
Forming processes in which the shape of the workpiece is changed incrementally (i. e. step-by-step) by repeated, local forming using geometrically simple dies which move relative to the workpiece. Open-die forging includes among others cogging, radial forging, rotary swaging, shell forging and rotational partial forging.
Rolling
Forming processes in which the material is formed between two or more rotating dies (rollers). Examples of rolling processes include; flat and profile rolling, spinning, flow forming and reduction rolling.
Ring-Rolling
Special rolling method for the manufacturing of seamless rings with related sub-methods such as; radial ring rolling, radial-axial ring rolling and axial closed die rolling.
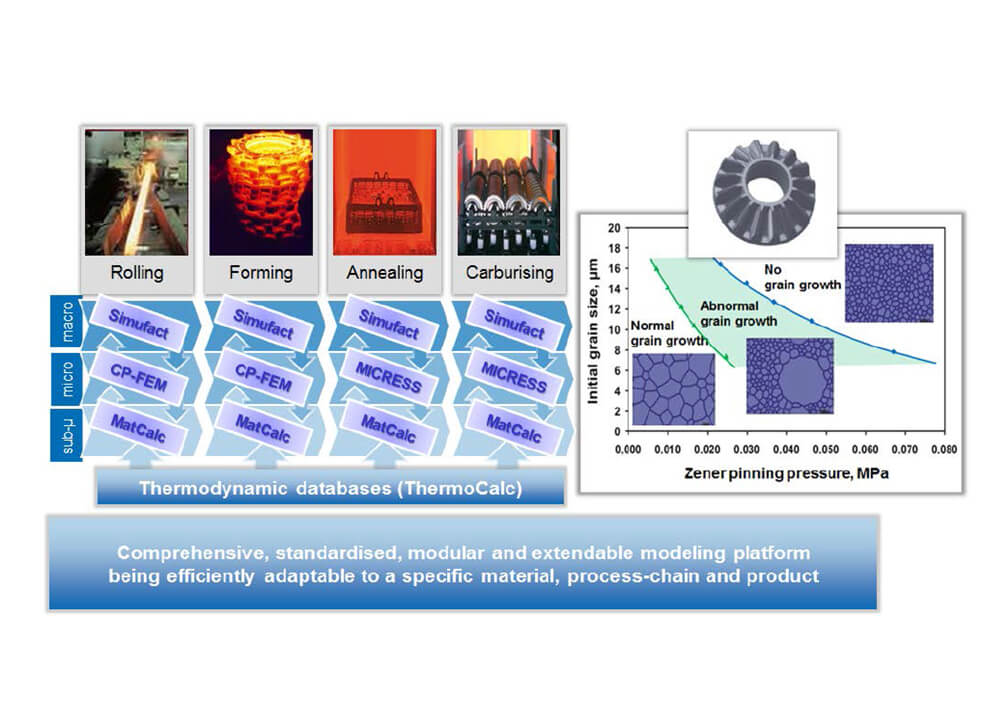
Methods in which, metallic workpieces (mainly steel pieces) are temporarily heated for the targeted improvement of the material’s properties.
Quench Temper
Quench temper enables the simulation of complex heat treatment processes with all necessary stages. In each of them the respective temperatures and heat transfer coefficients of resp. to dies and (furnace) environment can be specified in many ways as constant or changing.
Case Hardening
Case hardening enables the simulation of direct hardening processes with all necessary stages. In each of them the respective temperatures and heat transfer coefficients of resp. to dies and (furnace) environment can be specified in many ways as constant or changing.
Induction Heating
This process type allows the modelling of an inductive heating process and therefore a more precise estimation of the resulting temperature distibution.
Mechanical Joining
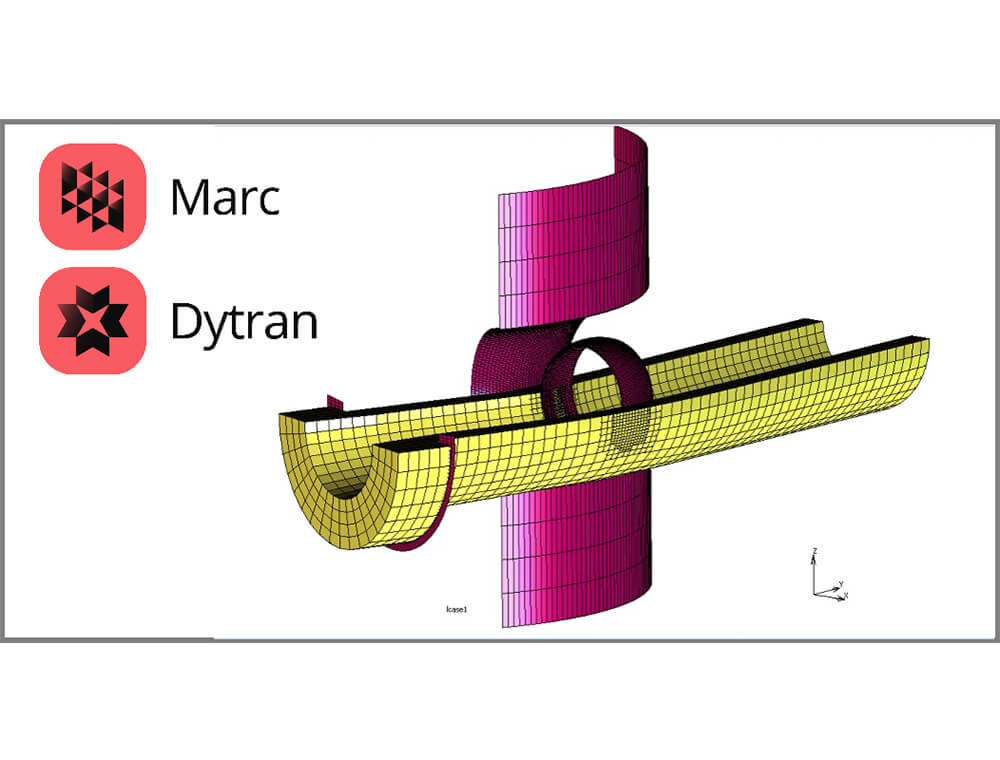
Forming processes that cause a mechanical interlock between the pieces. Mechanical joining includes riveting methods such as; punch riveting, self-piercing riveting and blind riveting, as well as clinching technologies such pressure joining, clinching and toxing.
Resistance Spot Welding
A pressure welding process during which the sheets are pressed together locally with the help of fitted copper electrode welding guns. The electrical current between the weld guns causes a heating and melting of the joining partners, creating a small circular welded area between them.
Pressure Welding
Methods in which, metallic workpieces (mainly steel pieces) are temporarily Pressure welding stands for a group of joining processes in which components are joined by heating and compression. Heat can be generated either via current (resistance welding) or by using friction (friction welding) for the targeted improvement of the material’s properties.
Your benefits with Simufact Forming
Design and optimise your forming process:
- Determine the optimal number and sequence of stages and process window with minimal material usage while ensuring a robust manufacturing process.
- Identify and eliminate potential manufacturing defects.
- Optimise tool life.
Simplicity – No expert knowledge required as the software solution is designed to be user-friendly, intuitive and process-oriented.
Sustainability – Save material, time and money by replacing expensive and time-consuming physical tests with virtual tests.
Research Projects
Learn more about Simufact Forming
Related Articles
Technical Article
High temperature quality inspection
White Paper
Reducing costs through virtual simulation
Flyer