Simufact Forming
Specialised forming simulation software for virtual testing and process design for component optimisation
Solución de software
Para procesos de conformado sin conocimientos especializados
A menudo, se requieren conocimientos especializados para operar entornos de simulación con el fin de construir y programar modelos complejos. Este no es el caso de Simufact Forming. El usuario no tiene que ocuparse de la física gris del proceso de conformado ni de los detalles específicos de la simulación. Simufact Forming es práctico y se puede aprender rápida y fácilmente. De este modo, el formador puede concentrarse en los detalles de sus procesos de conformado en lugar de en el software.

«Lo más sencillo posible, tan complejo como necesario»
La interfaz de usuario de Simufact Forming se desarrolló para ser sencilla, intuitiva y orientada al proceso. Esto convierte a Simufact Forming en una herramienta de diseño para el desarrollador de herramientas y procesos que soporta y facilita el trabajo diario del usuario. Con unos pocos clics, se pueden fijar y valorar todos los procesos de conformado estándar:
- Conformación en frío
- Forja en caliente
- Conformado de chapa metálica
- Rolling
- Rodamiento de anillos
- Forjado en matriz abierta
- Tratamiento de calor
- Unión mecánica
- Soldadura por presión
Haga clic aquí para saber más sobre los tipos de procesos individuales.
Sus ventajas con Simufact Forming
- Diseñe y optimice su proceso de conformado:
- Determine el número y la secuencia óptimos de etapas y la ventana del proceso con un uso mínimo de material, a la vez que garantiza un proceso de fabricación robusto.
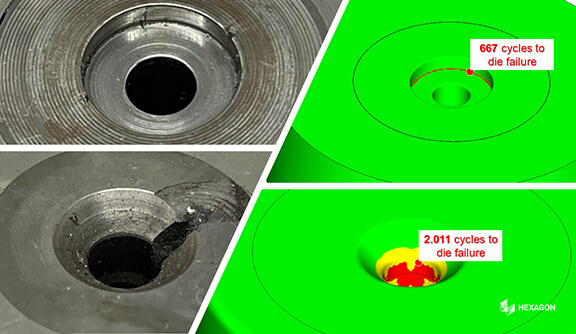
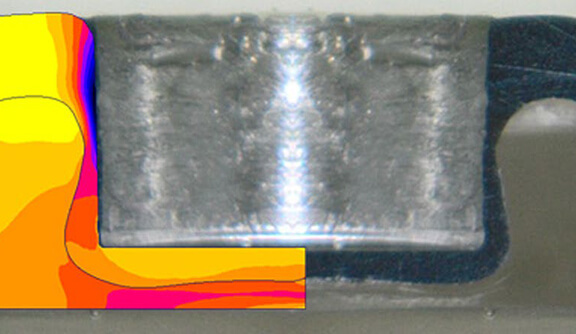
- Identifique y elimine posibles defectos de fabricación
- Optimice la vida útil del instrumento
- Sencillez: no se requieren conocimientos especializados, ya que la solución de software está diseñada para ser fácil de usar, intuitiva y orientada a los procesos.
- Sostenibilidad: ahorre material, tiempo y dinero reemplazando las costosas y lentas pruebas físicas por pruebas virtuales.
Obtenga más información sobre las características y las áreas de aplicación en el sitio web de Simufact.
Exactly the right forming process you need
Forming processes conducted significantly below the recrystallisation temperature of the material. These processes include typical upsetting and extrusion processes (e. g. for the production of bolts, nuts and rivets), but can also include coining, cold hobbing, thread rolling and last but not least drawing processes (e. g. wire drawing, tube drawing and profile drawing).
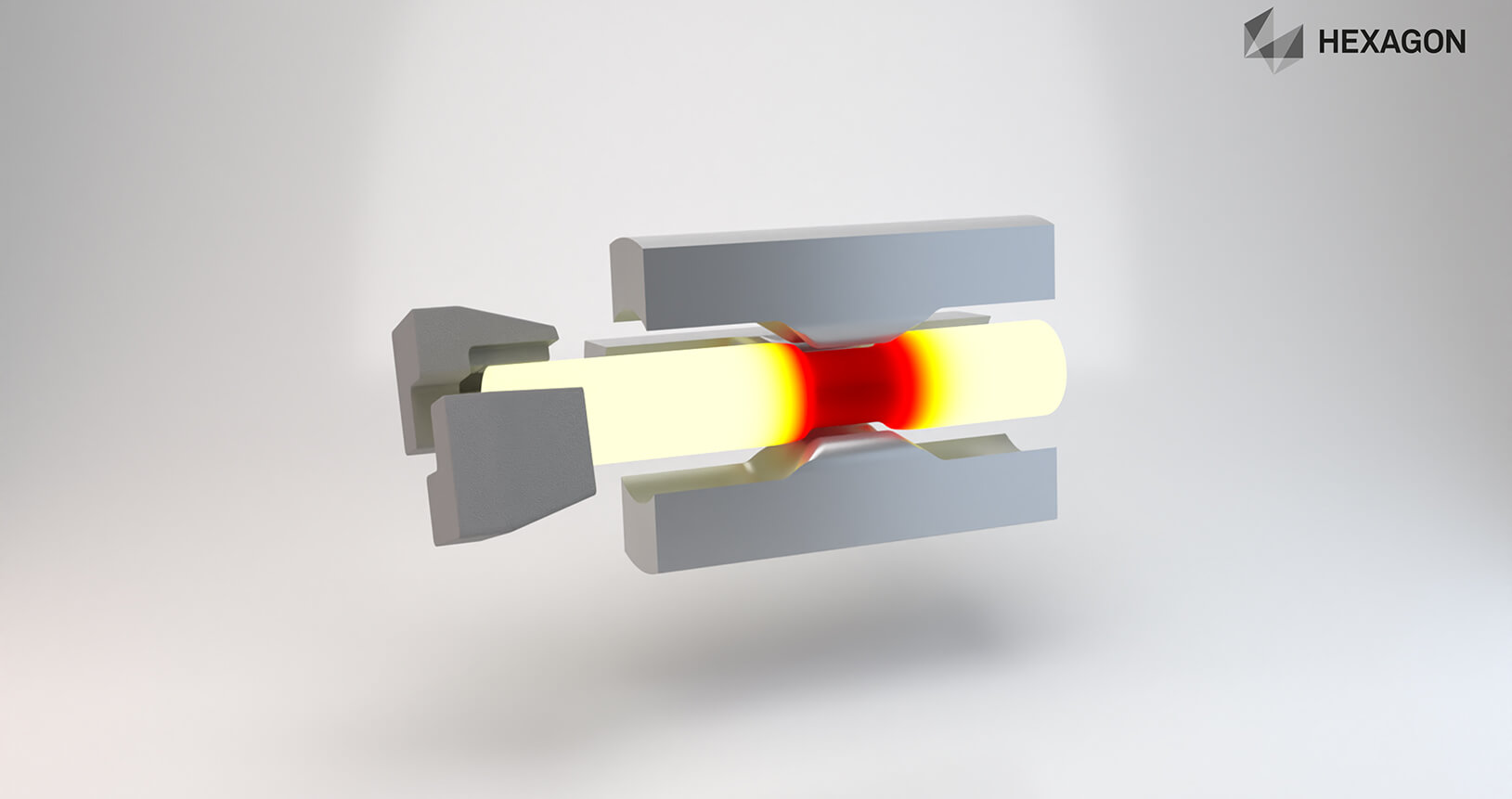
Forming processes conducted above the recrystallisation temperature of the material. A typical process is hot forging, including closed die hot forging, auxiliary processes such as heating and cooling, cutting processes and preform operations (e. g. upsetting, bending, forge rolling and cross wedge rolling) as well as extrusion processes.
Different methods of sheet metal forming can be used depending on the geometry of the desired part. Based on the characteristics of each deformation process, the forming engineer can choose between: Deep drawing, ironing, punching, bending, stamping, and a variety of other manufacturing processes. Due to the geometric complexity of the parts being manufactured, additional multistage forming that combines different processes is frequently required within a phase of production. Therefore, production is usually achieved by automated transfer or stage pressing, or by progressive tools.
Forming processes in which the shape of the workpiece is changed incrementally (i. e. step-by-step) by repeated, local forming using geometrically simple dies which move relative to the workpiece. Open-die forging includes among others cogging, radial forging, rotary swaging, shell forging and rotational partial forging.
Rolling
Forming processes in which the material is formed between two or more rotating dies (rollers). Examples of rolling processes include; flat and profile rolling, spinning, flow forming and reduction rolling.
Ring-Rolling
Special rolling method for the manufacturing of seamless rings with related sub-methods such as; radial ring rolling, radial-axial ring rolling and axial closed die rolling.
Methods in which, metallic workpieces (mainly steel pieces) are temporarily heated for the targeted improvement of the material’s properties.
Quench Temper
Quench temper enables the simulation of complex heat treatment processes with all necessary stages. In each of them the respective temperatures and heat transfer coefficients of resp. to dies and (furnace) environment can be specified in many ways as constant or changing.
Case Hardening
Case hardening enables the simulation of direct hardening processes with all necessary stages. In each of them the respective temperatures and heat transfer coefficients of resp. to dies and (furnace) environment can be specified in many ways as constant or changing.
Induction Heating
This process type allows the modelling of an inductive heating process and therefore a more precise estimation of the resulting temperature distibution.
Mechanical Joining
Forming processes that cause a mechanical interlock between the pieces. Mechanical joining includes riveting methods such as; punch riveting, self-piercing riveting and blind riveting, as well as clinching technologies such pressure joining, clinching and toxing.
Resistance Spot Welding
A pressure welding process during which the sheets are pressed together locally with the help of fitted copper electrode welding guns. The electrical current between the weld guns causes a heating and melting of the joining partners, creating a small circular welded area between them.
Pressure Welding
Methods in which, metallic workpieces (mainly steel pieces) are temporarily Pressure welding stands for a group of joining processes in which components are joined by heating and compression. Heat can be generated either via current (resistance welding) or by using friction (friction welding) for the targeted improvement of the material’s properties.
Your benefits with Simufact Forming
Design and optimise your forming process:
- Determine the optimal number and sequence of stages and process window with minimal material usage while ensuring a robust manufacturing process.
- Identify and eliminate potential manufacturing defects.
- Optimise tool life.
Simplicity – No expert knowledge required as the software solution is designed to be user-friendly, intuitive and process-oriented.
Sustainability – Save material, time and money by replacing expensive and time-consuming physical tests with virtual tests.
Research Projects
Learn more about Simufact Forming
Related Articles
Technical Article
High temperature quality inspection
White Paper
Reducing costs through virtual simulation
Flyer