WorkNC & WorkPLAN– the partners in Dixence’s software/machine tandem
Dixence - France
Contact us
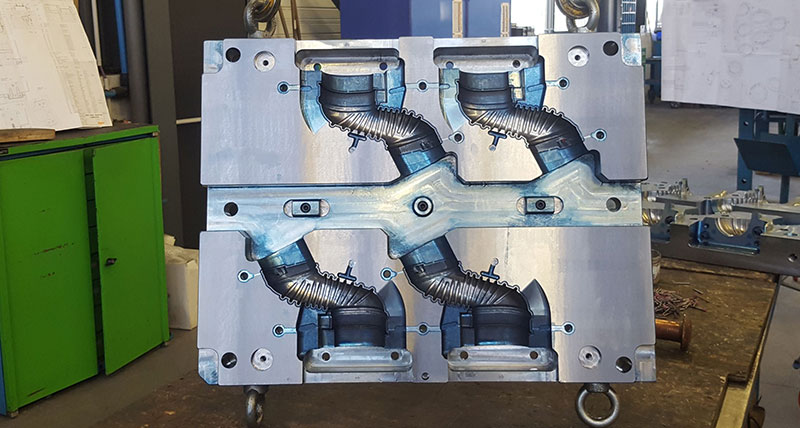
A company specialising in industrial rubber injection moulds and cold runner blocks for the automotive sector uses WorkNC to create 3+2 axis toolpath programs across a range of eight CNC machine tools and WorkPLAN to consolidate a variety of information from sales orders to invoices.
Dixence is an SME operating with around 30 staff out of a 1,500 m2 workshop and 500 m2 engineering department at Erbray, in Western France.
Their main business is designing and manufacturing tooling equipment, and manufacturing moulds for all-rubber bonded inserts, and plastic, metal and rubber parts. Managing Director Gérard Beloeil says these can be injection, compression, regulated transfer or cold plate moulds produced in different grades of steel; pre-treated, hardened, and with a special coating.
“The finished parts are used to support gearboxes, engines, exhaust pipes, suspension systems, engine sealings, and soundproofing.”
Working for major suppliers of rubber parts around the world, including France, Germany, Spain, USA, UK, Russia, Turkey, Portugal, around 80 per cent of their output is for automotive contracts, with the rest going to customers in the energy, cosmetics and railway industries. They have recently made a REP V710 L 50 rubber injection press available for validating moulds produced for the international market. At the customers' request, moulds are tested directly on-site at Dixence avoiding any costly part returns…giving a real guarantee of quality.
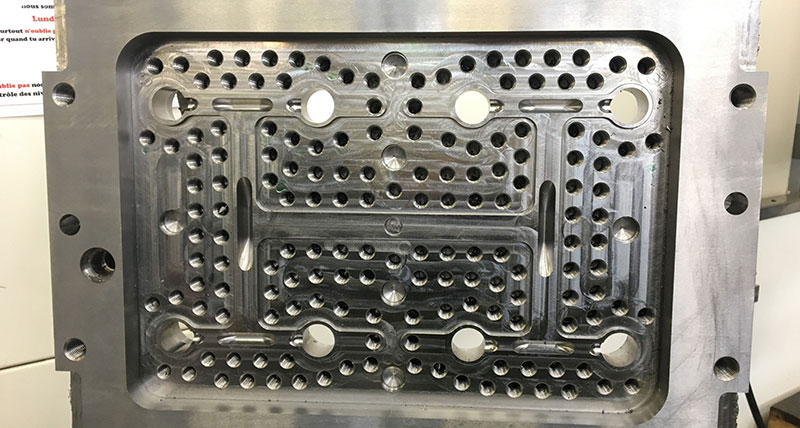 About three-quarters of the total production goes through WorkNC, which Milling Sector Manager Fabrice Provost says is fundamental to ensuring that the moulds coming off the machine tools are of the high precision required. “The software’s 3D functions are particularly important to us as we use 3+2 axis machining, but can’t program 3D manually. And since new enhancements have been made for 2D operations such as manual and semi-automatic drilling, we use all 2D toolpaths as they’re now more flexible.”
About three-quarters of the total production goes through WorkNC, which Milling Sector Manager Fabrice Provost says is fundamental to ensuring that the moulds coming off the machine tools are of the high precision required. “The software’s 3D functions are particularly important to us as we use 3+2 axis machining, but can’t program 3D manually. And since new enhancements have been made for 2D operations such as manual and semi-automatic drilling, we use all 2D toolpaths as they’re now more flexible.”
WorkNC programs three Huron and two Mazak vertical milling centres, and two Mazak horizontal palletised milling centres to produce the moulds and blocks, along with one HSM milling centre for machining electrodes. “It’s this software/machine tandem that allows us to achieve a high level of precision. The two go hand in hand.”
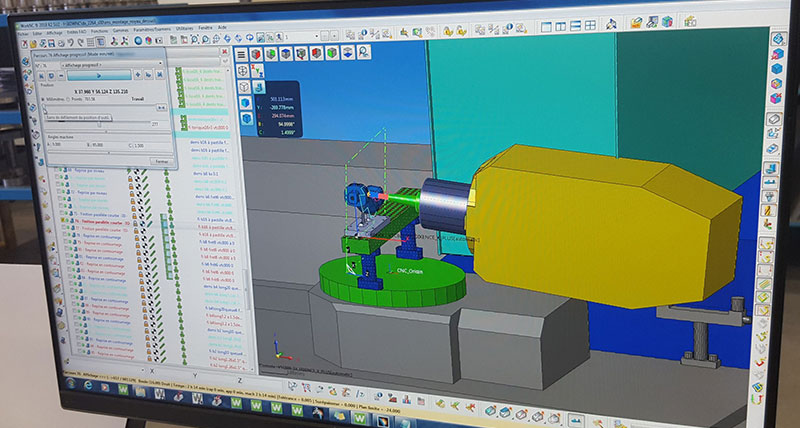
Initially, the mould CAD files are sent to the Engineering Department to check the project’s feasibility and to determine the different steps required to produce the tool. Each part of the mould is identified and listed, and a bill of materials is inserted into WorkPLAN. Based on that information, a set of documents is generated, containing full details about the mould, which will be used by the purchasing document and shopfloor, allowing work to start on tooling elements. Machining information about the mould’s individual components means the milling and turning team can assign them to specific machines, and the files are opened in WorkNC for the toolpaths to be programmed.
“Our programmers often use standard WorkNC toolpaths such as 3-axis Finishing and Contour Remachining, which we find perfect for producing a high-quality finish on curved surfaces where there are no right angles. And the comprehensive Global Roughing functions are extremely efficient, producing exactly the results we need.”
Even though some parts they produce are similar, all moulds manufactured by Dixence are different. Generally, they make two new mould tools each week. They also produce one cold runner block, which is positioned on the mould, meaning they can multiply the number of injection points for rubber-based components. “An important feature of our process is that we design a cold runner block for each project, so it is specific to each mould. This offers a means of reducing material costs for our customers, especially as rubber can’t be recycled.”
He says using WorkNC has improved productivity and reduced errors on finished parts. “The workshop functions round the clock, unsupervised during the night. With the full range of WorkNC toolpaths, all our machines will soon be able to run during the night, increasing productivity even further over a 24-hour period.”
Dixence also use WorkNC’s sister brand, WorkPLAN as their production control system. Gérard Beloeil says they previously worked with an Access database and paper-based invoicing. “But with ever-increasing production levels we needed to avoid duplicating data processing.”
 With WorkPLAN they consolidate all information, such as sales orders, purchase orders, time management, delivery notes and invoices, which is relative to each project. “We’ve also got full traceability on purchasing, raw materials – including quantity and cost – and purchasing material for individual mould component, which means we can make quick and accurate decisions.
With WorkPLAN they consolidate all information, such as sales orders, purchase orders, time management, delivery notes and invoices, which is relative to each project. “We’ve also got full traceability on purchasing, raw materials – including quantity and cost – and purchasing material for individual mould component, which means we can make quick and accurate decisions.
A number of modules are particularly important to them:
Job Management, which manages sales related tasks and administration, from order confirmation through to delivery…allowing easy access to all project-related documents.
The Purchasing module includes their forecast purchase budget based on the bills of material directly imported into WorkPLAN, along with supplier quotations. “We can easily monitor and control raw material costs and determine minimum stock levels.”
The Time Management function allows real time monitoring of machine utilisation, the status of outsourced tasks, and the remaining time required to finish a task. “We often have similar tools to produce, so we can simply look for a previous project, copy it, and make the necessary modifications.”
And thanks to the Sales Activity module, order forms and invoices are generated with just a few clicks, as all the necessary information has already been fed into the system.
“This avoids duplicated data entry errors, and means we can monitor invoices daily, and chase payment to maintain a reasonable cash flow.”
Dixence is an SME operating with around 30 staff out of a 1,500 m2 workshop and 500 m2 engineering department at Erbray, in Western France.
Their main business is designing and manufacturing tooling equipment, and manufacturing moulds for all-rubber bonded inserts, and plastic, metal and rubber parts. Managing Director Gérard Beloeil says these can be injection, compression, regulated transfer or cold plate moulds produced in different grades of steel; pre-treated, hardened, and with a special coating.
“The finished parts are used to support gearboxes, engines, exhaust pipes, suspension systems, engine sealings, and soundproofing.”
Working for major suppliers of rubber parts around the world, including France, Germany, Spain, USA, UK, Russia, Turkey, Portugal, around 80 per cent of their output is for automotive contracts, with the rest going to customers in the energy, cosmetics and railway industries. They have recently made a REP V710 L 50 rubber injection press available for validating moulds produced for the international market. At the customers' request, moulds are tested directly on-site at Dixence avoiding any costly part returns…giving a real guarantee of quality.
 About three-quarters of the total production goes through WorkNC, which Milling Sector Manager Fabrice Provost says is fundamental to ensuring that the moulds coming off the machine tools are of the high precision required. “The software’s 3D functions are particularly important to us as we use 3+2 axis machining, but can’t program 3D manually. And since new enhancements have been made for 2D operations such as manual and semi-automatic drilling, we use all 2D toolpaths as they’re now more flexible.”
About three-quarters of the total production goes through WorkNC, which Milling Sector Manager Fabrice Provost says is fundamental to ensuring that the moulds coming off the machine tools are of the high precision required. “The software’s 3D functions are particularly important to us as we use 3+2 axis machining, but can’t program 3D manually. And since new enhancements have been made for 2D operations such as manual and semi-automatic drilling, we use all 2D toolpaths as they’re now more flexible.”WorkNC programs three Huron and two Mazak vertical milling centres, and two Mazak horizontal palletised milling centres to produce the moulds and blocks, along with one HSM milling centre for machining electrodes. “It’s this software/machine tandem that allows us to achieve a high level of precision. The two go hand in hand.”
Initially, the mould CAD files are sent to the Engineering Department to check the project’s feasibility and to determine the different steps required to produce the tool. Each part of the mould is identified and listed, and a bill of materials is inserted into WorkPLAN. Based on that information, a set of documents is generated, containing full details about the mould, which will be used by the purchasing document and shopfloor, allowing work to start on tooling elements. Machining information about the mould’s individual components means the milling and turning team can assign them to specific machines, and the files are opened in WorkNC for the toolpaths to be programmed.
“Our programmers often use standard WorkNC toolpaths such as 3-axis Finishing and Contour Remachining, which we find perfect for producing a high-quality finish on curved surfaces where there are no right angles. And the comprehensive Global Roughing functions are extremely efficient, producing exactly the results we need.”
Even though some parts they produce are similar, all moulds manufactured by Dixence are different. Generally, they make two new mould tools each week. They also produce one cold runner block, which is positioned on the mould, meaning they can multiply the number of injection points for rubber-based components. “An important feature of our process is that we design a cold runner block for each project, so it is specific to each mould. This offers a means of reducing material costs for our customers, especially as rubber can’t be recycled.”
He says using WorkNC has improved productivity and reduced errors on finished parts. “The workshop functions round the clock, unsupervised during the night. With the full range of WorkNC toolpaths, all our machines will soon be able to run during the night, increasing productivity even further over a 24-hour period.”
Dixence also use WorkNC’s sister brand, WorkPLAN as their production control system. Gérard Beloeil says they previously worked with an Access database and paper-based invoicing. “But with ever-increasing production levels we needed to avoid duplicating data processing.”
 With WorkPLAN they consolidate all information, such as sales orders, purchase orders, time management, delivery notes and invoices, which is relative to each project. “We’ve also got full traceability on purchasing, raw materials – including quantity and cost – and purchasing material for individual mould component, which means we can make quick and accurate decisions.
With WorkPLAN they consolidate all information, such as sales orders, purchase orders, time management, delivery notes and invoices, which is relative to each project. “We’ve also got full traceability on purchasing, raw materials – including quantity and cost – and purchasing material for individual mould component, which means we can make quick and accurate decisions.A number of modules are particularly important to them:
Job Management, which manages sales related tasks and administration, from order confirmation through to delivery…allowing easy access to all project-related documents.
The Purchasing module includes their forecast purchase budget based on the bills of material directly imported into WorkPLAN, along with supplier quotations. “We can easily monitor and control raw material costs and determine minimum stock levels.”
The Time Management function allows real time monitoring of machine utilisation, the status of outsourced tasks, and the remaining time required to finish a task. “We often have similar tools to produce, so we can simply look for a previous project, copy it, and make the necessary modifications.”
And thanks to the Sales Activity module, order forms and invoices are generated with just a few clicks, as all the necessary information has already been fed into the system.
“This avoids duplicated data entry errors, and means we can monitor invoices daily, and chase payment to maintain a reasonable cash flow.”
Concluding, Gérard Beloeil says: “With all data about material quantities, costs, and time spent on tasks, recorded in WorkPLAN, we can quickly calculate the cost budget of our moulds, and progressively improve our profitability.”
