Hexagon simulation increases PCI-SCEMM productivity
NCSIMUL moves powertrain parts supplier into industry 4.0 era “ahead of time”
Contact us
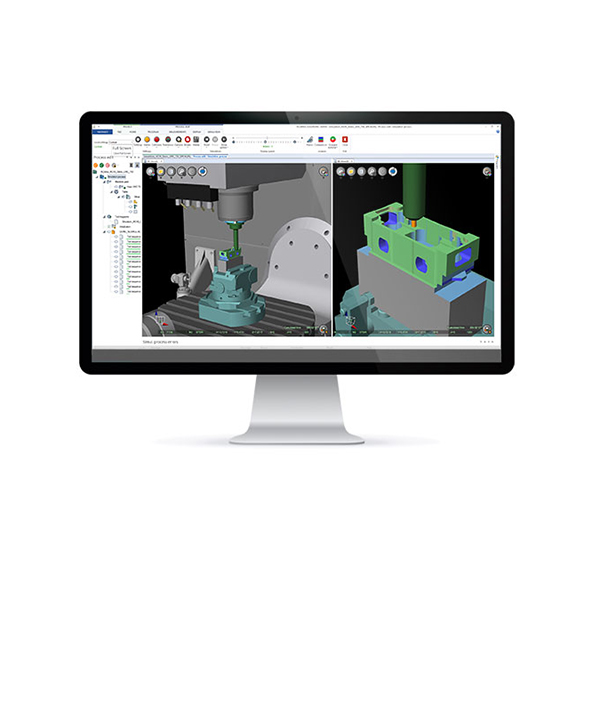
Simulation software from Hexagon, that reads the post-processed G-code to identify machining tool paths, literally brought a specialist manufacturer into the 21st Century, and now helps improve productivity by up to 30 per cent.
Hervé Damon, Head of Machining Process Studies at PCI-SCEMM, says they first invested in NCSIMUL in the late 1990s. “Since then we’ve continued to improve our methodologies, and thanks to the team at Hexagon, we’re further improving our controllers and virtual machines to keep pace with the evolution of Fanuc and Siemens numerical controls, and physical machines.”
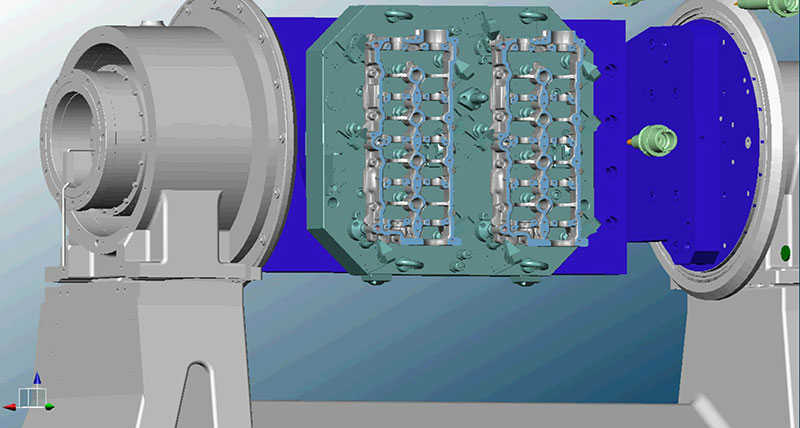
PCI-SCEMM creates machining solutions for the mass production of conventional powertrain parts, such as cylinder heads and gearboxes; along with battery-trays and e-housings for e-Mobility powertrains. It is located near to the Manufacture d'Armes de Saint-Étienne – a former French state-owned manufacturing company in Saint-Étienne on an industrial site hosting the Higher Institute of Performance Techniques engineering school.
According to Hervé Damon, the company moves in the “hyper competitive international environment” of high speed production of automotive parts, which he describes as “the most demanding industry.”
And having used NCSIMUL’s market-leading simulation functionality for more than 20 years to perfect its machining programs, he says it enables PCI-SCEMM to guarantee cycle times, lead times, quality and overall cost for all operations. “It helps us achieve productivity gains of between 20 and 30 per cent compared to just using a conventional CAD/CAM system.
“Our service to customers is based on the combination of high performance machining centres associated with innovative and robust machining processes. Simulation with NCSIMUL allows us to propose more profitable technical and economical solutions requiring fewer machines, giving us a real competitive advantage.”
He says they opted for NCSIMUL after rigorous comparison with other packages on the market. “Each of our projects is unique, and a real challenge. Therefore, we need to create tailor-made machining programs that exploit 100 per cent of the machines’ capacities; that adapt 100 per cent to the parts to be machined; and that take into account 100 per cent of the customer’s constraints. Therefore, we over-optimise each line of code to ensure fast and efficient set-up. We code directly in ISO, and then validate the program with NCSIMUL.
 “Thanks to systematic simulation upstream, during pre-studies, then downstream, during programming, all processes simulated in NCSIMUL are deployed without collision, with no accessibility issues, no unnecessary travel, and with high-performance machining ranges.”
“Thanks to systematic simulation upstream, during pre-studies, then downstream, during programming, all processes simulated in NCSIMUL are deployed without collision, with no accessibility issues, no unnecessary travel, and with high-performance machining ranges.”
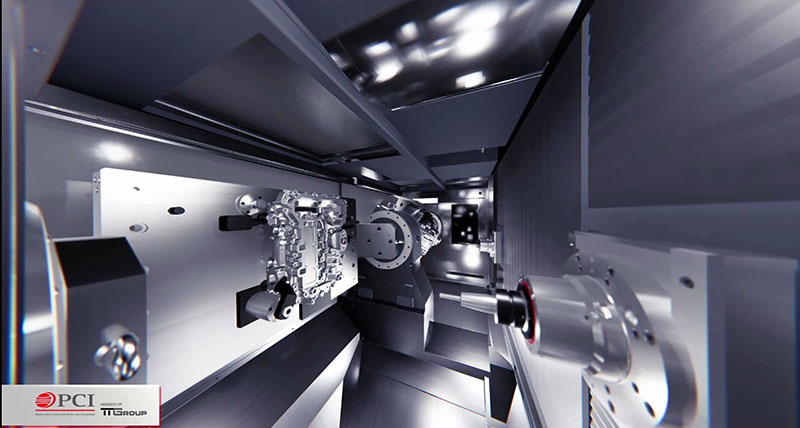
The simulations serve as a technical link from the pre-studies, through the various development phases, to the start of production. Hervé Damon says their knowledge in defining and implementing machining processes including methods, ranges, cutting tools, fixtures, programming and simulation, is at the heart of their strategic business.
About 50 programs were produced during 2019, using proven methodologies, based on around 100 versions of virtual machines.
“Implementing these methodologies, and integrating simulation and numerical validation has brought us, ahead of time, into the era of Industry 4.0. For example, our virtual machines are real digital twins, which allow us, via ISO code, to link the virtual world to the physical world. Thanks to the flexibility of custom manual programming, we can take into account and optimise the use of the signals from all the physical sensors integrated in our machines – such as part temperature, hard sensing (which is a PCI-SCEMM patent), and spindle power.
“We’re also able to integrate fine corrections from metrology results, either manually or automatically, via inertial control software,” concludes Hervé Damon.
Hervé Damon, Head of Machining Process Studies at PCI-SCEMM, says they first invested in NCSIMUL in the late 1990s. “Since then we’ve continued to improve our methodologies, and thanks to the team at Hexagon, we’re further improving our controllers and virtual machines to keep pace with the evolution of Fanuc and Siemens numerical controls, and physical machines.”
PCI-SCEMM creates machining solutions for the mass production of conventional powertrain parts, such as cylinder heads and gearboxes; along with battery-trays and e-housings for e-Mobility powertrains. It is located near to the Manufacture d'Armes de Saint-Étienne – a former French state-owned manufacturing company in Saint-Étienne on an industrial site hosting the Higher Institute of Performance Techniques engineering school.
According to Hervé Damon, the company moves in the “hyper competitive international environment” of high speed production of automotive parts, which he describes as “the most demanding industry.”
And having used NCSIMUL’s market-leading simulation functionality for more than 20 years to perfect its machining programs, he says it enables PCI-SCEMM to guarantee cycle times, lead times, quality and overall cost for all operations. “It helps us achieve productivity gains of between 20 and 30 per cent compared to just using a conventional CAD/CAM system.
“Our service to customers is based on the combination of high performance machining centres associated with innovative and robust machining processes. Simulation with NCSIMUL allows us to propose more profitable technical and economical solutions requiring fewer machines, giving us a real competitive advantage.”
He says they opted for NCSIMUL after rigorous comparison with other packages on the market. “Each of our projects is unique, and a real challenge. Therefore, we need to create tailor-made machining programs that exploit 100 per cent of the machines’ capacities; that adapt 100 per cent to the parts to be machined; and that take into account 100 per cent of the customer’s constraints. Therefore, we over-optimise each line of code to ensure fast and efficient set-up. We code directly in ISO, and then validate the program with NCSIMUL.
 “Thanks to systematic simulation upstream, during pre-studies, then downstream, during programming, all processes simulated in NCSIMUL are deployed without collision, with no accessibility issues, no unnecessary travel, and with high-performance machining ranges.”
“Thanks to systematic simulation upstream, during pre-studies, then downstream, during programming, all processes simulated in NCSIMUL are deployed without collision, with no accessibility issues, no unnecessary travel, and with high-performance machining ranges.”The simulations serve as a technical link from the pre-studies, through the various development phases, to the start of production. Hervé Damon says their knowledge in defining and implementing machining processes including methods, ranges, cutting tools, fixtures, programming and simulation, is at the heart of their strategic business.
About 50 programs were produced during 2019, using proven methodologies, based on around 100 versions of virtual machines.
“Implementing these methodologies, and integrating simulation and numerical validation has brought us, ahead of time, into the era of Industry 4.0. For example, our virtual machines are real digital twins, which allow us, via ISO code, to link the virtual world to the physical world. Thanks to the flexibility of custom manual programming, we can take into account and optimise the use of the signals from all the physical sensors integrated in our machines – such as part temperature, hard sensing (which is a PCI-SCEMM patent), and spindle power.
“We’re also able to integrate fine corrections from metrology results, either manually or automatically, via inertial control software,” concludes Hervé Damon.